High quality canine and rat Sertoli Cells available for researcher
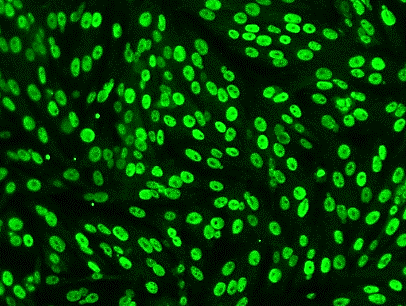
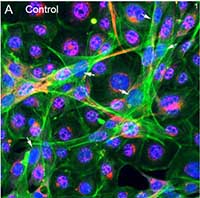
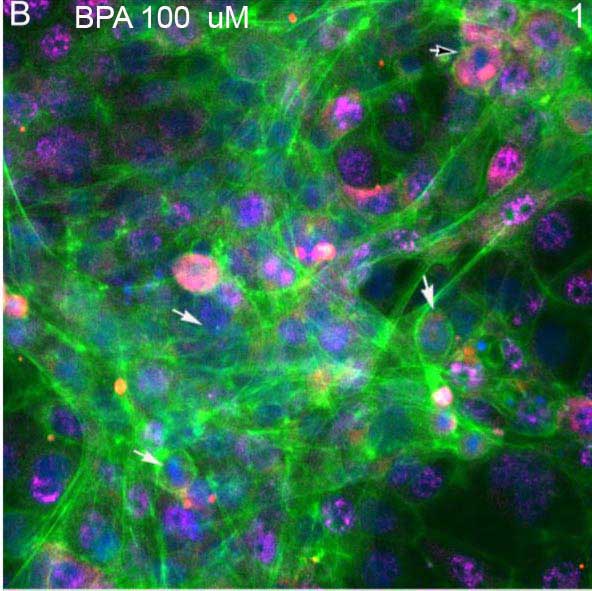
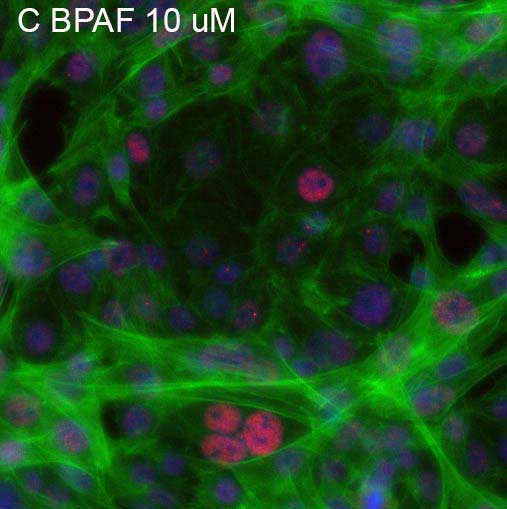
Sertoli cells play critical roles in regulating spermatogenesis and testis development by providing structural and nutritional support. This study aimed to develop a standard protocol for canine Sertoli cell isolation and culture; and characterize its biological features, functionality, and application of compound toxicity testing. Canine testicles were received from the neuter clinic, and three-step of enzymatic digestion was applied to isolate Sertoli cells. We characterized the growth and purity of Sertoli cells with the expression of SOX9, GATA4, and Clusterin. In addition, we selected cadmium as a model toxicant to evaluate the toxic responses in the newly established Sertoli cells using High-content Analysis (HCA). With our optimized protocol, the purity of isolated Sertoli cells was above 95%, as determined with Sertoli cell-specific protein markers of SOX9 and GATA4. More importantly, primary Sertoli cell populations could be expanded rapidly in vitro, passaged (up to seven), and cryopreserved. The HCA-based assay revealed that cadmium at 1 μM induced both disruptions of cytoskeletal and DNA damage responses. Furthermore, we established an HCA assay with the newly isolated and optimized culture of canine Sertoli cells to evaluate the epigenetic markers of histone modification. We found cadmium-induced differential changes in histone modifications H3Me3K9, H3Me3K36, H4Me3K20, and H4acK5. In summary, we have established the standardized protocol to produce canine Sertoli cells with Sertoli cell-specific phenotype. The isolation and expansion of large quantities of canine Sertoli cells will provide broad applications in studying male infertility, reproductive toxicology, testicular cancer, and cell therapy.
Read More Request a quota